How to Establish a Proper Internal Linking Strategy
Search engines like links. They make it possible for both users and search engines spiders to navigate a website and understand its content. Internal links play a few important roles for your site, some of which you probably aren’t aware of, but all roles you should know and understand for better SEO.
Did you know that links can pass value? What about links adding to organizations hierarchy? Ever think about the type of user experience created by strategic link placement?
In this article, we’ll be discussing what internal linking is, how you can master it for SEO, and how to test your current internal linking strategy.
What is Internal Linking?
An internal link is a link that targets (links to) a different page on the same domain. For example, you’re currently on https://alchemymarketing.com/the-seo-checklist/proper-internal-linking, so if I add a link to alchemymarketing.com/the-seo-checklist, it will take you to a different page on the same domain. These pages are now connected to one another through this link.
How does Internal Linking Affect SEO?
Proper internal linking helps users and search engines better understand a website, which directly affects SEO.
Think of internal links like portals to move from one spot on your site to another. Crawlers from Google start on your homepage and travel through your site by jumping through every available portal to get to the next page. Without internal linking, these crawlers are going to get stuck. They probably won’t be too pleased about it either, which can hurt your ranking.
Link Value
Search engines like Google look at the link value of a page. If a page has a lot of backlinks, it will be seen as valuable in Google’s eyes. And the value doesn’t stop there. If that page then links internally to other pages on the same domain, they’ll gain some of that page’s value as well.
Think of it as an endorsement from a popular page to a smaller one. Search engines think, “This is a strong page and it’s linking to this other page so that one must be good as well.”
However, Google notices how many internal links you’ve put on a page and adjusts the amount of link value accordingly. So you can’t just throw hundreds of links on your homepage and expect them all to get a lot of value. It doesn’t work like that.
Link value is how valuable the link is in Google’s eyes. This is determined by the number of backlinks the link has.
Bonus Points: Value can be transfered to other pages that are linked to internally from the highly valued page.
Nofollow Tags
Now that we know that internal links pass link value, we need to decide whether or not we actually want to pass that value.
Link value is a limited resource. If you don’t want to pass on the link value to a page you aren’t using to create conversions (Think login pages and confirmation pages.) you can add a nofollow tag.
<a href=”alchemymarketing.com/login” rel=”nofollow”>Click here to log in</a>
A nofollow tag tells search engines that you don’t want any of the link value passed along to that page of the site. It may not make a huge difference, but every little bit counts in the SEO world.
Hierarchy
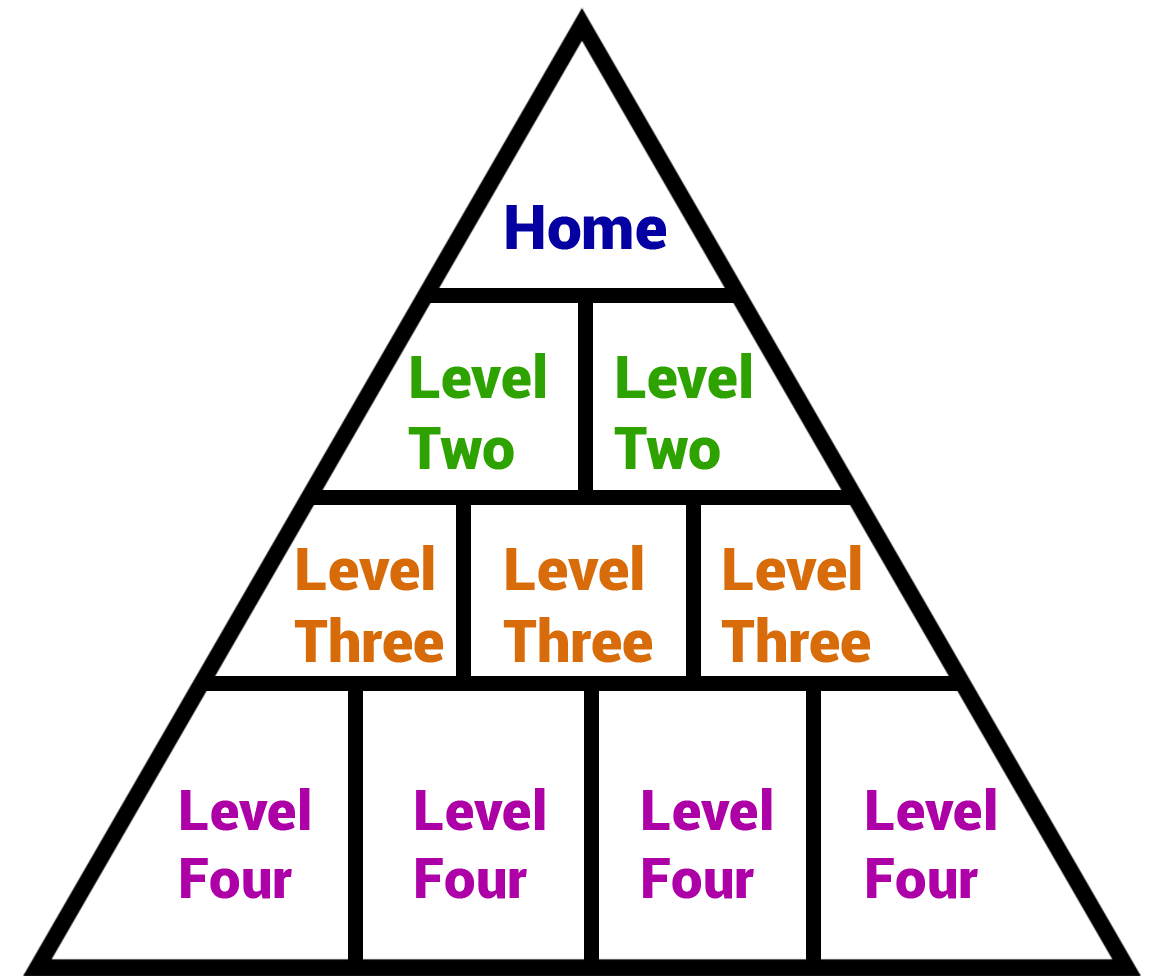
Establishing a logical hierarchy of your website is done using internal links. Your website should function like a pyramid, with the homepage being the top. Every link brings the user to a deeper level than they were before.
This also helps search engines spiders to understand your website and index it properly.
Once the spider goes to your homepage, it will be able to follow all of the links to completely navigate the whole site.
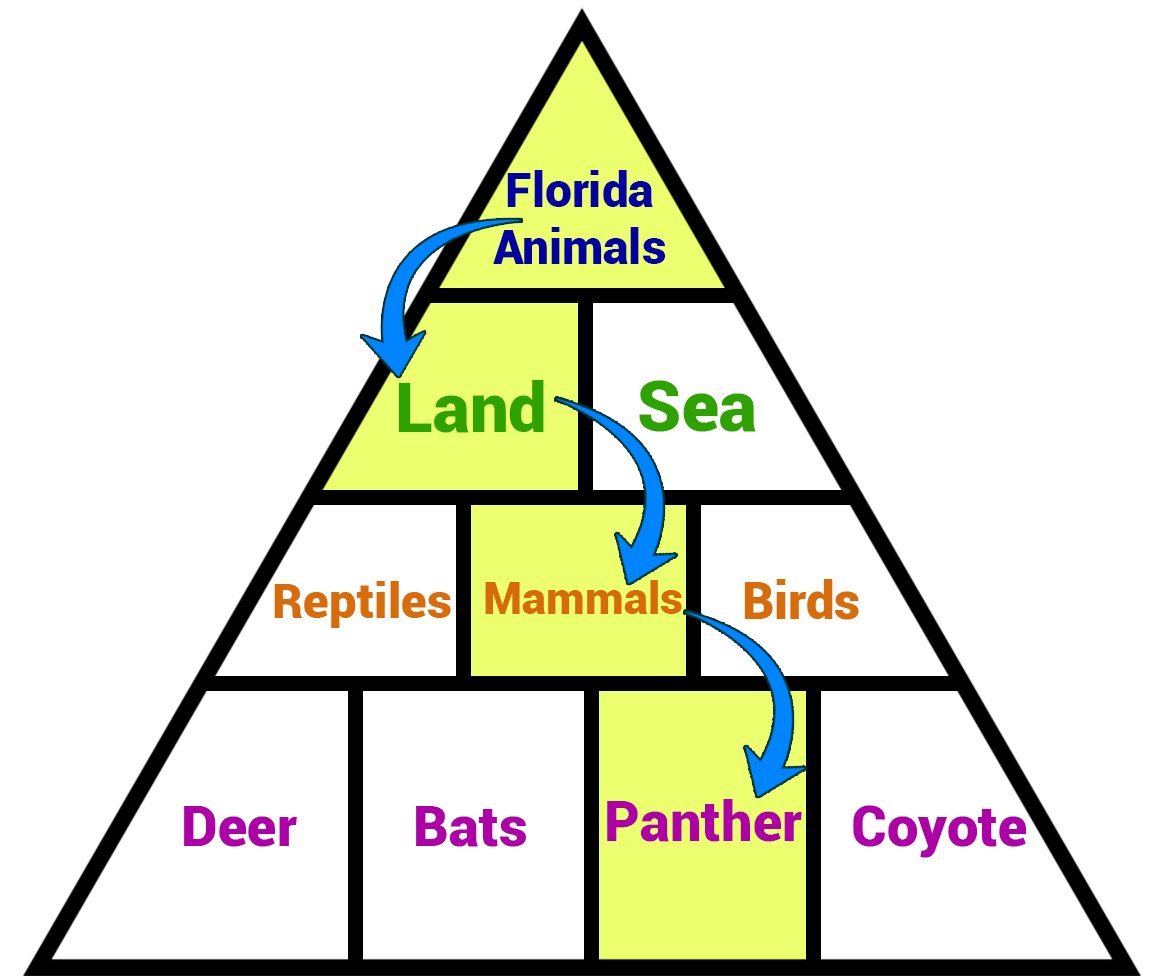
The pyramid should start with the most important and broad information and move downward towards more specific information. For example, if you have a website about the different animal species that live in Florida, a user’s pathway from your homepage to an article may look like this.
Category Pages
A great way to ensure that your site is organized in a logical way is by using category pages. This is especially useful for blogs. Every post that you write can be categorized into a specific category and the category can be linked to. That way, if the user wants to learn about that specific topic, they can just click the link and view all of the articles for that category.
You can find the categories of each of our articles tagged under the author’s photo, so there’s always a link back to the categories that the topic fits into.
Ensure that Every Page is Linked to
A page that doesn’t have any links pointing to it is called an orphan page. You should go through your site and make sure that every page that you want users and search engines finding is linked to.
There’s no way for users or spiders to find a page unless it’s linked to at least once on your site.
One way to make sure that every page on your site is indexed is uploading a sitemap. Read our tutorial on sitemaps to learn more.
Test Your Internal Linking
Depending on the size of your site, checking every link to every page may take a while, but it’s worth it to ensure a proper linking structure. If your site is too big, consider reading our tutorial on fixing 404 errors.
A good linking structure should only take two or three clicks to get to any page from any other page on the site.
If you have a page of any use or importance that takes more than two or three clicks to get to from your home page, consider restructuring the links to be more accessible.